New research shows that babies expect leaders to intervene and stop transgressions

Infants at 17 months of age expect their leaders and those in authority to act when one member of a group transgresses against another, but do not expect those who are not leaders or in authority to respond.
The findings, which were recently published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, add to a growing body of evidence that children have a well-developed understanding of social hierarchies and power dynamics, from a younger age than previously thought.
University of Illinois psychology professor Renée Baillargeon led the research which was conducted in Baillargeon’s Infant Cognition Lab by graduate student Maayan Stavans.
“We know that adults expect the leaders of social groups to intervene to stop within-group transgressions,” Ms Stavans said. “We wanted to know how early those expectations appear in human development, so we examined the question in very young children.”
Using a well-established method that gives insight into the reasoning of children too young to fully express themselves verbally, the researchers tracked how long children stare at different events to gain insight into what they think.
In a series of experiments, 120 infants watched bear puppets while sitting in the lap of a parent. Some of the children watched scenarios involving a protagonist that two other bears treated as a leader, and some saw a protagonist that appeared to have no authority over the other two bears.
In all the scenarios, the protagonist presented the other bears with two toys for them to share, but one bear quickly grabbed both toys, leaving none for the other bear. Next, the protagonist either rectified this transgression by redistributing one of the toys from the wrongdoer bear to the victim bear, or the protagonist ignored the transgression by approaching each bear without redistributing a toy.
“The scenarios differed in the status of the protagonist – was she a leader or not? – and in the protagonist’s response to the transgression – did she rectify the situation or ignore it?” Dr Baillargeon said.
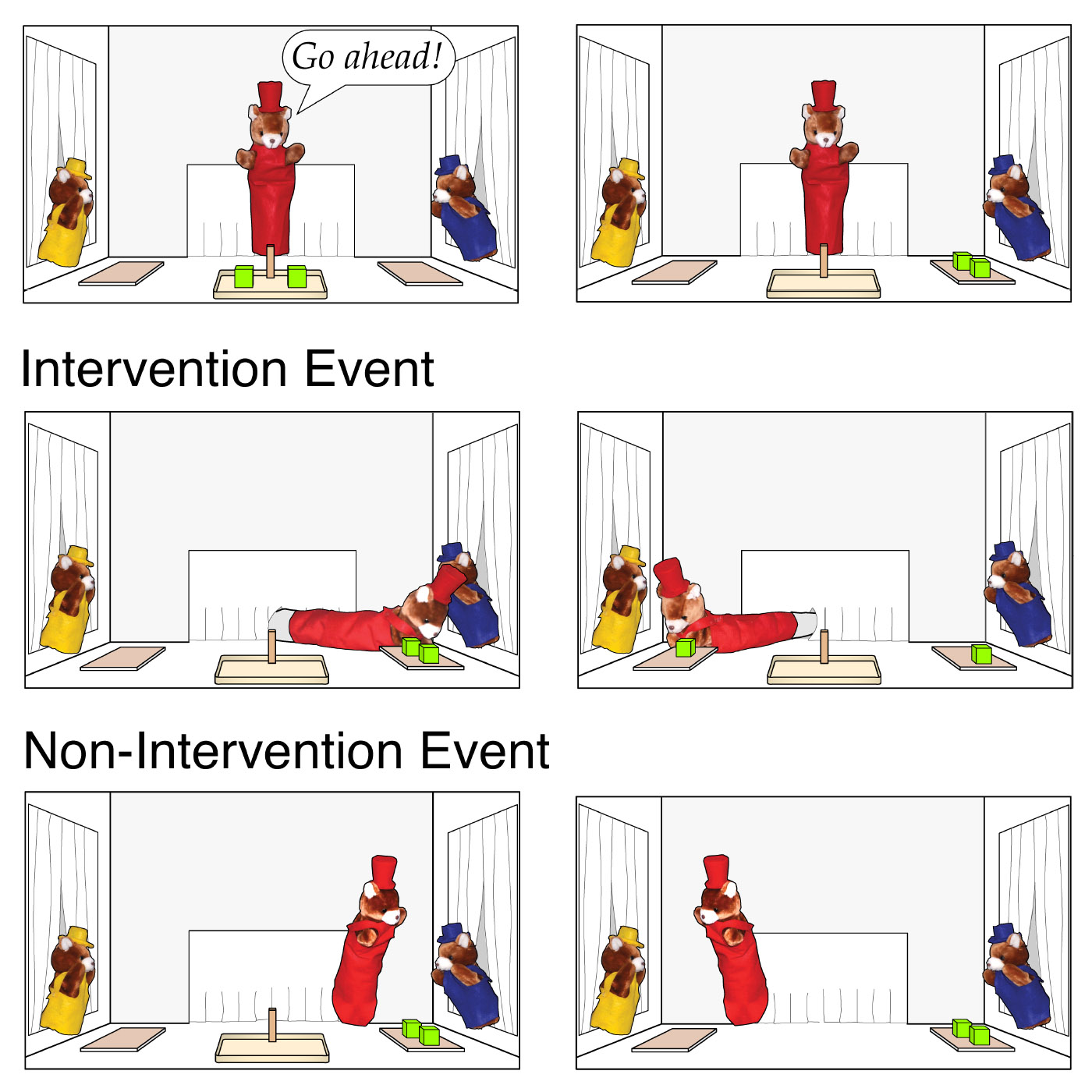
Infants in the study watched as a protagonist bear, in red, either intervened to redress a wrong perpetrated by the bear in blue against the bear in yellow, or ignored the transgression.
Graphic courtesy Renée Baillargeon
“Infants stared longer when the leader ignored the wrongdoing than when she rectified it,” Dr Baillargeon said. “This suggests that infants expected the leader to intervene and right the wrong in her group, and were surprised when she took no such action.”
The children also stared longer at the wrongdoer bear than they stared at the victim bear when the leader ignored the transgression, as if something about the wrongdoer would explain the leader’s reluctance to correct her.
The infants did not appear to be surprised when a protagonist who was not a leader failed to redress the same wrongdoing.
In two experiments, infants consistently stared longer when leaders failed to act against wrongdoers, Ms Stavans said. “But they held no particular expectation for intervention from nonleaders.”
In a third experiment, one of the bears announced that she did not want a toy and the other bear took both toys. The infants in this experiment stared longer when the leader intervened to make sure that each bear had one toy.
“It was as if the infants understood that in this case there was no transgression, so they viewed it as overbearing for the leader to redistribute one of the toys to a bear who had made it clear she didn’t want one,” Ms Stavans said.
The findings provide new evidence that infants can reason about leaders, Dr Baillargeon said.
“We knew from previous work that children this age have specific ideas about how followers will behave toward their leaders,” she said. “Now we see that they also have complementary expectations about how leaders will behave toward their followers.”
To read the Infants expect leaders to right wrongs research, please see here.
Popular

Quality
Practice
Provider
Research
ECEC in focus - Una Springwood’s intergenerational initiative brings young and old together through connection and care
2025-06-30 10:00:45
by Contributed Content

Provider
Practice
Quality
Research
Aboriginal Education Strategy drives early learning and school success in South Australia
2025-07-01 09:55:12
by Fiona Alston

Workforce
Policy
Quality
Research
Inclusive Practice Framework set to strengthen inclusion in early childhood settings
2025-06-24 11:37:00
by Isabella Southwell











