Understanding Children
Babies learn language from their mothers while in utero, research finds

Freya Lucas
Apr 25, 2022
Save
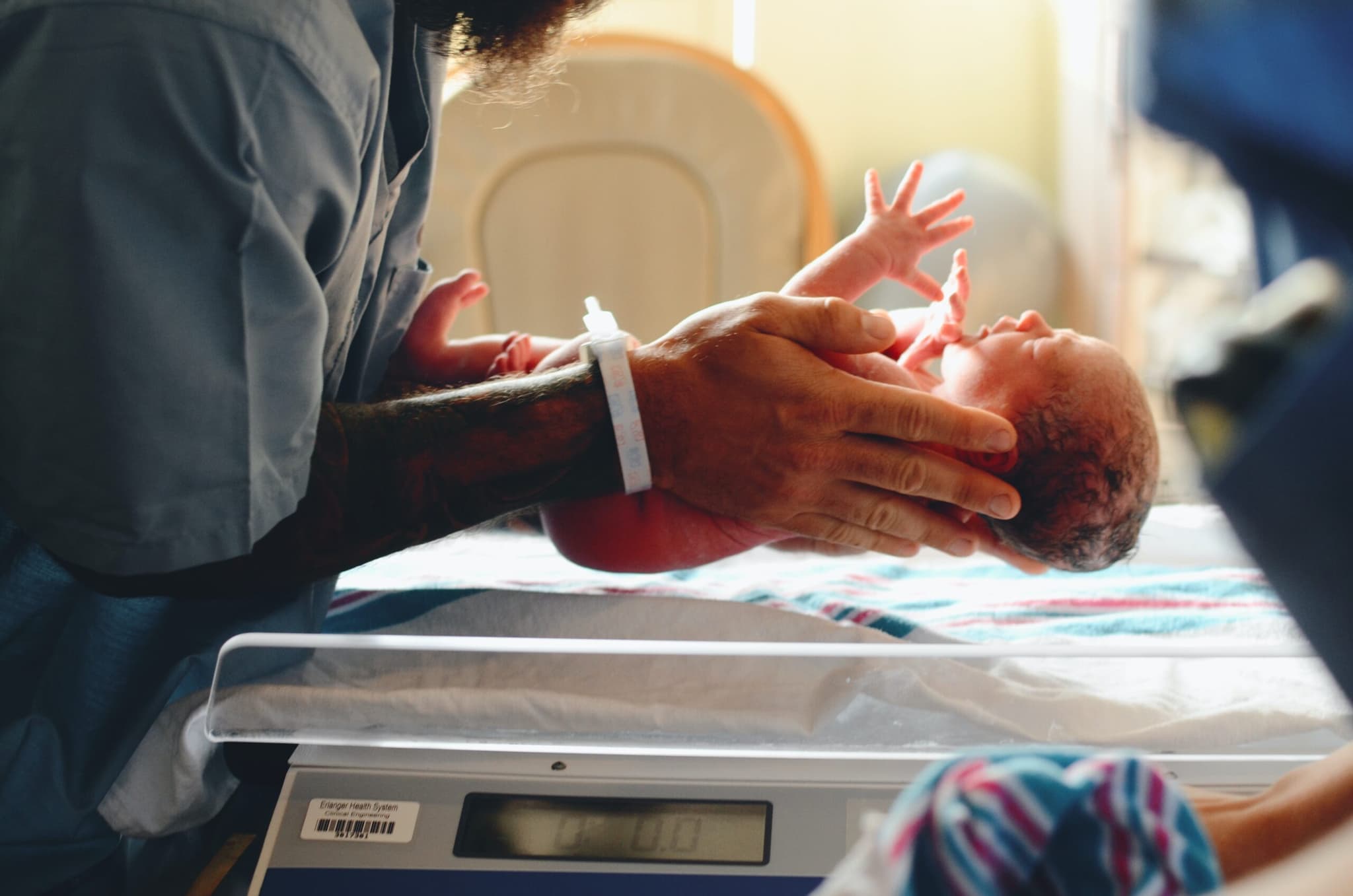
Unborn babies are listening to their mothers talk during the last ten weeks of pregnancy, and are able to differentiate between sounds from their native language and a foreign language within hours of birth, research has shown.
The study indicates that babies begin absorbing language while still in the womb, earlier than previously thought.Sensory and brain mechanisms for hearing are developed at 30 weeks of gestational age, and the new study officially confirms that mothers “have first dibs on influencing the child’s brain,” Patricia Kuhl, co-author and co-director of the Institute for Learning & Brain Sciences at the University of Washington explained.
“The vowel sounds in her speech are the loudest units and the fetus locks onto them.”
Previously, researchers had shown that newborns are born ready to learn and begin to discriminate between language sounds within the first months of life, but there was no evidence that language learning had occurred in utero.
“This is the first study that shows fetuses learn prenatally about the particular speech sounds of a mother’s language,” said Christine Moon, lead author and a professor of psychology at Pacific Lutheran University added. “This study moves the measurable result of experience with speech sounds from six months of age to before birth.”
To gather the results 40 infants, all around 30 hours old, were studied in Tacoma and Stockholm, Sweden. While still in the nursery, the babies listened to vowel sounds in their native tongue and in foreign languages.
Their interest in the sounds was captured by how long they sucked on a pacifier that was wired into a computer measuring the babies’ reaction to the sounds. Longer or shorter sucking for unfamiliar or familiar sounds is evidence for learning, because it indicates that infants can differentiate between the sounds heard in utero.
In both countries, the babies at birth sucked longer for the foreign language than they did for their native tongue.
The researchers say that infants are the best learners, and discovering how they soak up information could give insights on lifelong learning. “We want to know what magic they put to work in early childhood that adults cannot,” Ms Kuhl said. “We can’t waste that early curiosity.”
To access the study please see here.
Don’t miss a thing
Related Articles